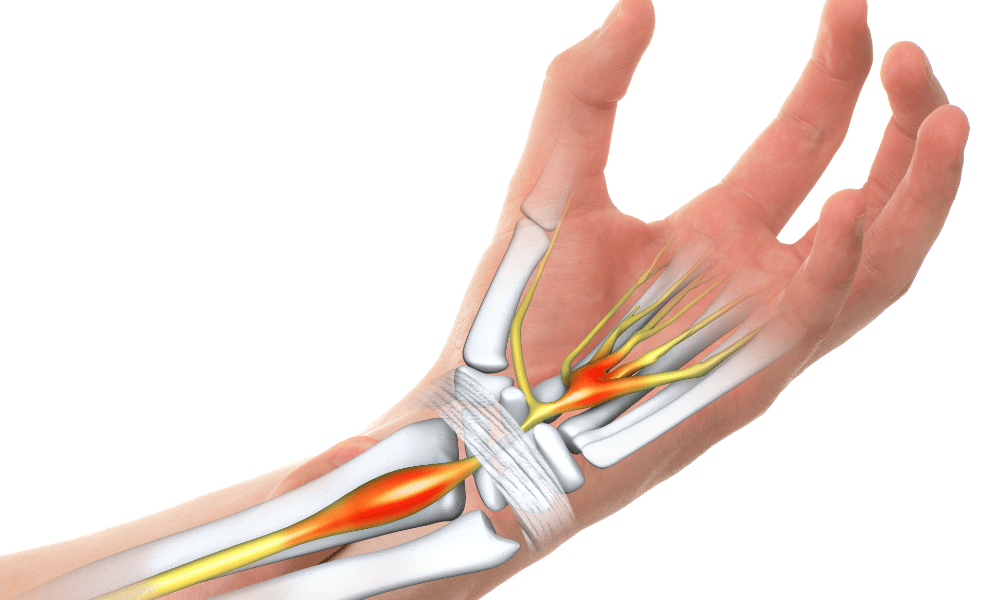
Strategies to Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition characterized by pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the wrist, becomes compressed. Several factors, including repetitive hand movements, poor ergonomics, and underlying medical conditions, can contribute to the development of CTS. In this science-oriented blog post, we will explore evidence-based strategies to help you avoid Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and maintain healthy hands and wrists.
- Practice Good Ergonomics
Maintaining proper ergonomics in your workspace is crucial for preventing CTS. Ensure that your chair, desk, and computer setup are ergonomically designed to support neutral wrist positions. Keep your forearms parallel to the floor, your wrists straight, and your fingers relaxed while typing or using a mouse. Adjust your keyboard height, use wrist rests, and position your monitor at eye level to reduce strain on the wrists and promote healthy hand posture.
- Take Frequent Breaks and Stretch
Prolonged and repetitive hand movements can increase the risk of CTS. Take regular breaks from activities that involve repetitive hand motions, such as typing or using handheld devices. During these breaks, perform gentle stretching exercises to relieve tension in the wrists and fingers. Simple exercises like wrist flexion and extension, finger spreads, and wrist circles can help maintain flexibility and reduce the strain on the median nerve.
- Use Proper Typing Techniques
Typing is a common activity that can contribute to CTS. To avoid excessive strain on your wrists, use a light touch when typing and let your fingers glide over the keys without excessive force. Maintain a relaxed hand posture and avoid resting your wrists on hard surfaces while typing. Consider using an ergonomic keyboard or wrist supports to promote neutral wrist alignment.
- Take Care of Your Hands and Wrists
Taking care of your hands and wrists is essential for preventing CTS. Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the strain on your joints. Avoid prolonged exposure to cold temperatures, as cold hands are more susceptible to injury. Wear protective gear, such as gloves, when engaging in activities that involve repetitive hand motions or exposure to vibrations.
- Strengthen and Stretch Your Forearm Muscles
Strengthening and stretching the muscles of your forearms can help prevent CTS. Perform exercises that target the forearm muscles, such as wrist curls, forearm twists, and grip strengthening exercises. These exercises can improve muscle endurance and flexibility, reducing the risk of strain and compression on the median nerve.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Certain lifestyle factors can impact your risk of developing CTS. Avoid smoking, as it can reduce blood flow and impair tissue healing. Maintain a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support overall health and reduce inflammation in the body. Stay hydrated to promote tissue health and prevent stiffness in the joints.
- Use Proper Hand Tools and Equipment
Using appropriate hand tools and equipment can reduce the strain on your hands and wrists. Choose tools with ergonomic handles and grips that allow for a neutral wrist position. When using hand tools, distribute the force evenly across your hand and avoid excessive gripping or twisting motions.
- Seek Prompt Medical Attention
If you experience symptoms such as pain, numbness, or tingling in your hands or wrists, seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention and treatment can prevent the progression of CTS and alleviate symptoms. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and suggest modifications to your daily activities to reduce strain on the wrists.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is crucial for maintaining healthy hands and wrists and preserving your quality of life. By practicing good ergonomics, taking frequent breaks and stretching, using proper typing techniques, caring for your hands and wrists, strengthening and stretching your forearm muscles, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, using proper hand tools, and seeking prompt medical attention, you can reduce your risk of developing CTS. Prioritize the health of your hands and wrists and incorporate these evidence-based strategies to keep them strong, flexible, and pain-free.